Kabelik GmbH is offering additionally to the acquisition and data processing of airborne remote sensing data also the data analysis services. Below are some examples.
LIDAR classification
The classification of lidar point cloud returns in accordance with a
classification scheme to identify the type of target from which each
lidar return is reflected. The process allows future differentiation
between bare-earth terrain points, water, noise, vegetation, buildings,
other man-made features and objects of interest.
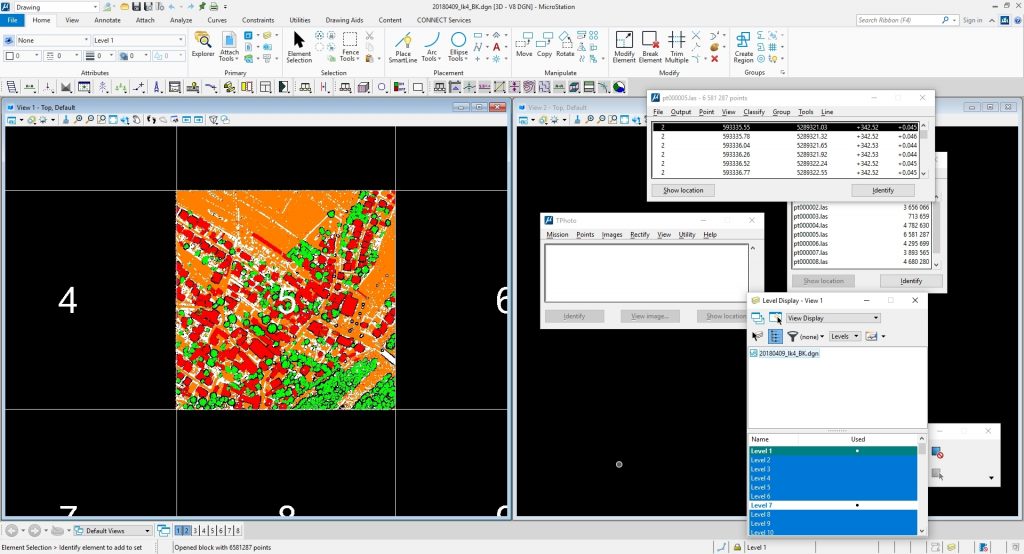
At classification of a pointcloud, every data point is classified into a
class. There are several classes for instance ground, vegetation,
building, rail, etc. (see ASPRS las specification). In the image below
you can see orange is ground, vegetation is green, buildings are red and
not classified is white.
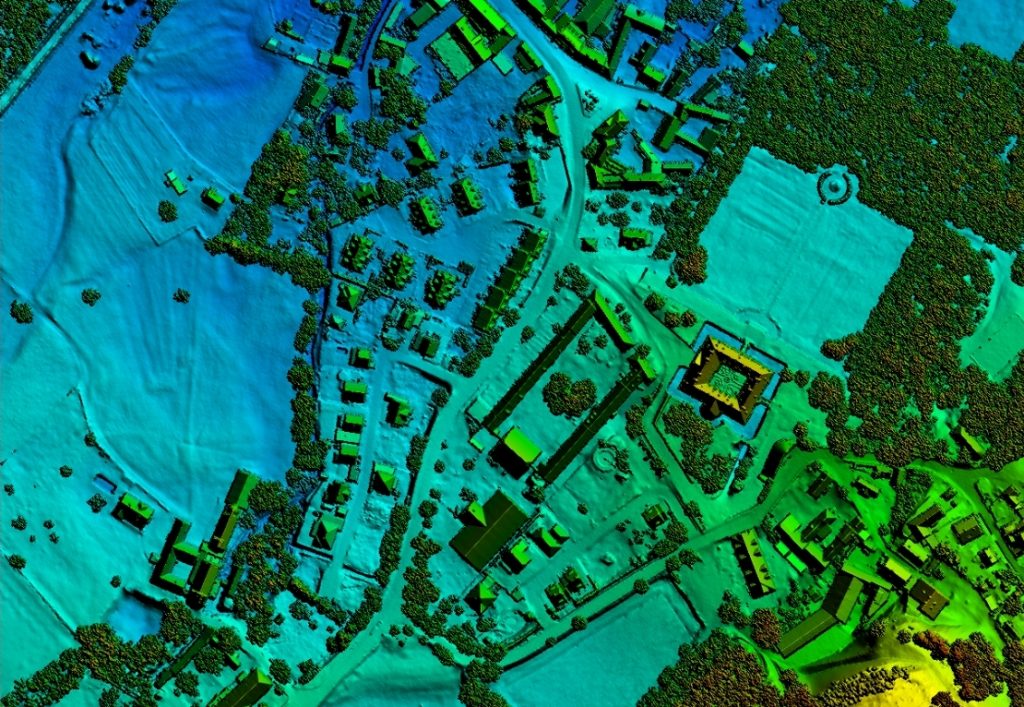
DSM
The digital surface model (DSM) is a collection of three dimensional points to represent or derive a surface of all applicable terrain and features including: buildings, bridges, roads, vegetation and hydrology.
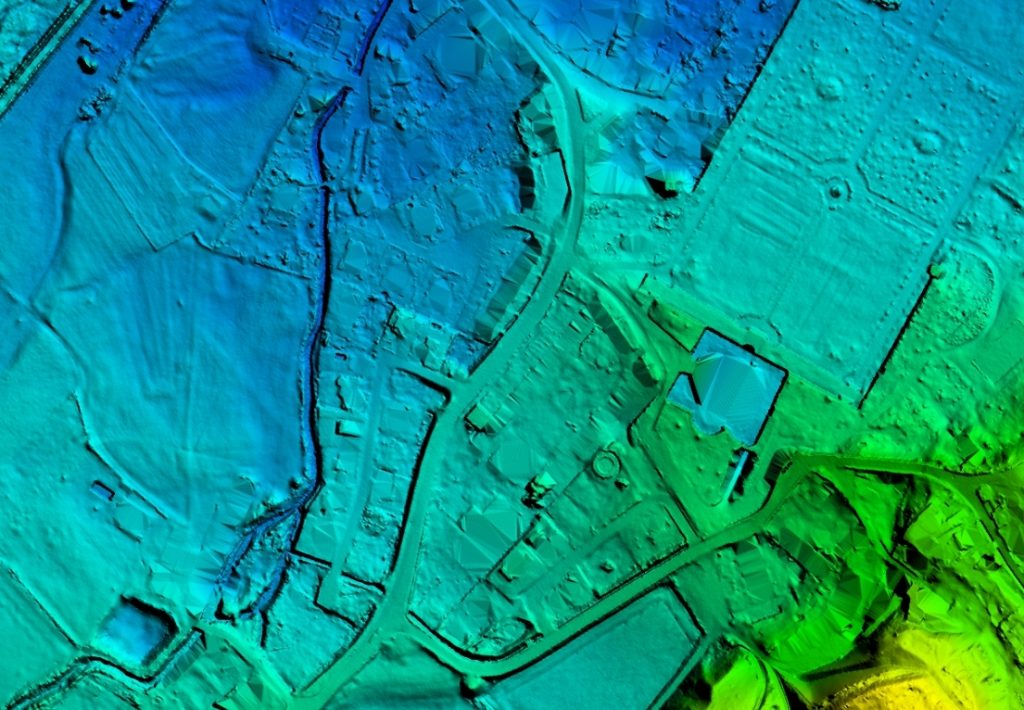
DTM
The digital terrain model (DTM) is a collection of three dimensional points in a grid or random arrangement to represent or derive a Bare Earth surface.
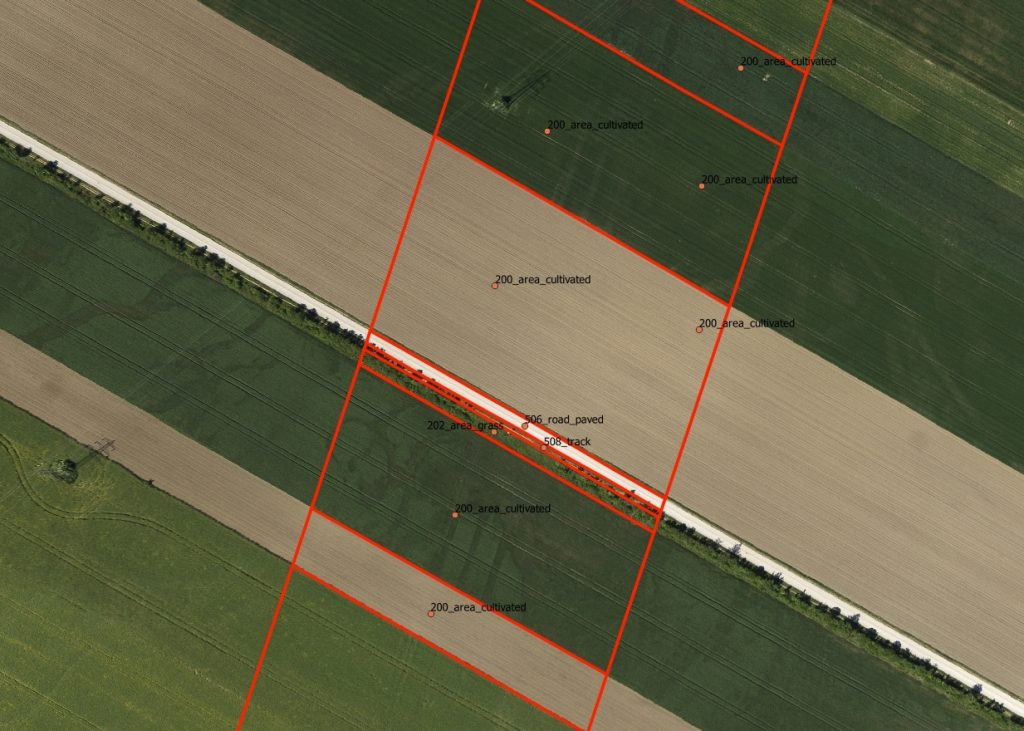
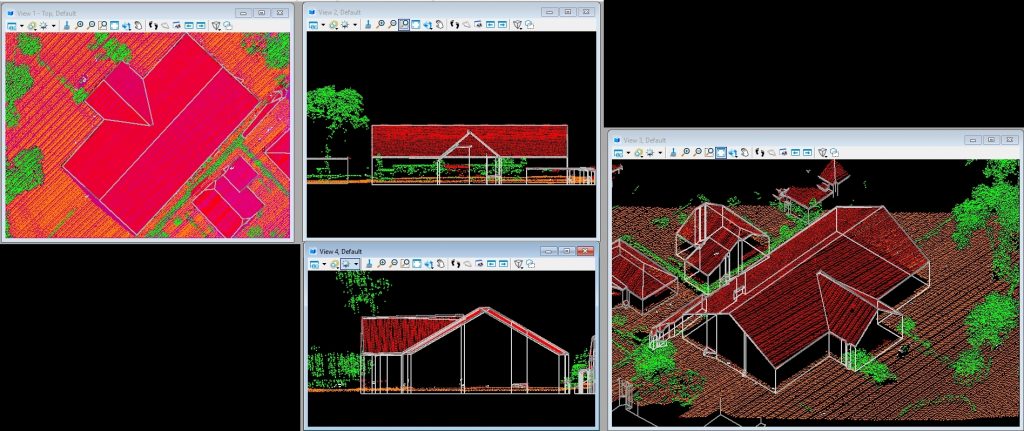
3D Vectorisation & Polygons
LIDAR and orthophoto data is used to extract three dimensional vector information in a predefined data structure. Thereafter this vector information is used to build polygons.


Building vectorisation
Change detection
TBA
Danger Objects
TBA
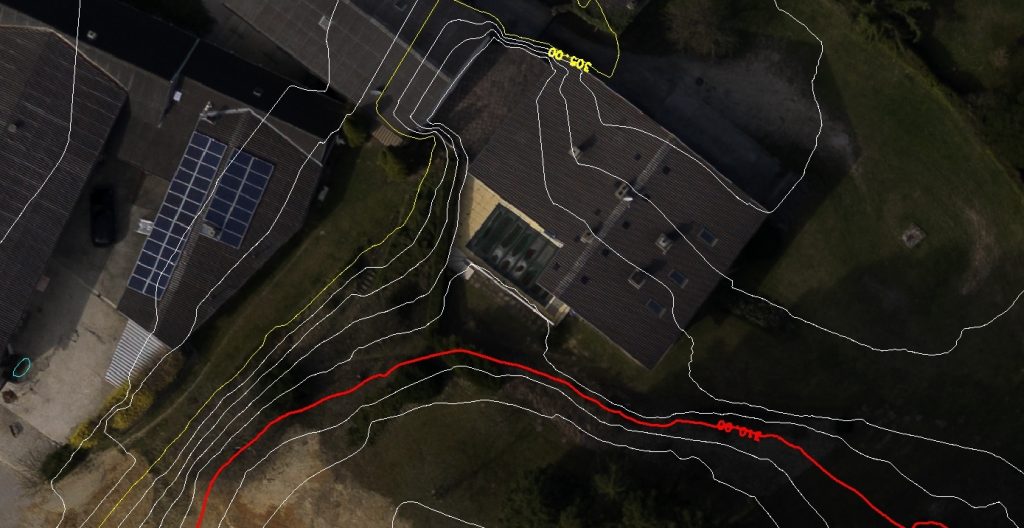
Contour lines
A line map demarking lines of constant elevation across a terrain surface. It is often included in a topographical map.

Volume + Mass calculation
TBA